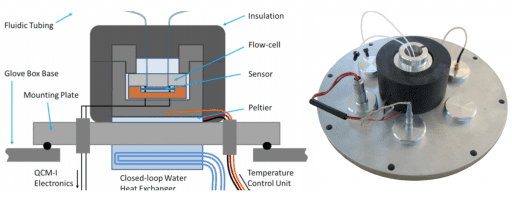
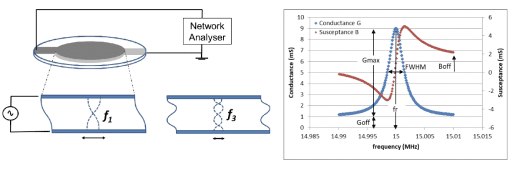
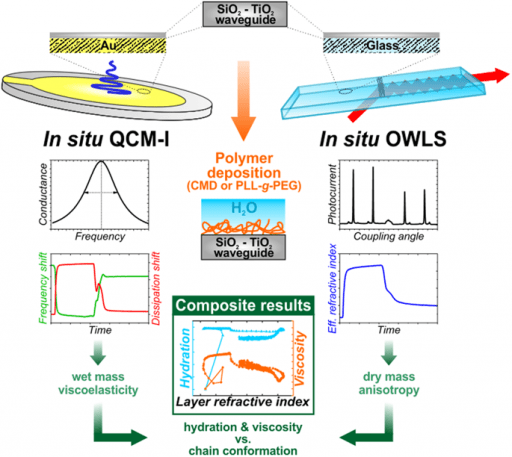
Fluidic Configurations for QCM-I / QCM-D
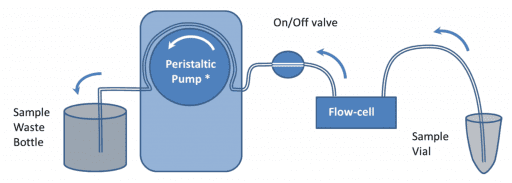
Pump Flow Control with Manual Sample Introduction It is recommended that samples are introduced to the QCM-I flow-cells using a pump to control the flow. In the simplest setup, shown in figure 1, a peristaltic pump* is used to suck buffer directly from a beaker or other container. Sample is introduced to the flow-cell by […]